YES! Encrypted Traffic Can (and Must) Be Classified
Encryption Trends
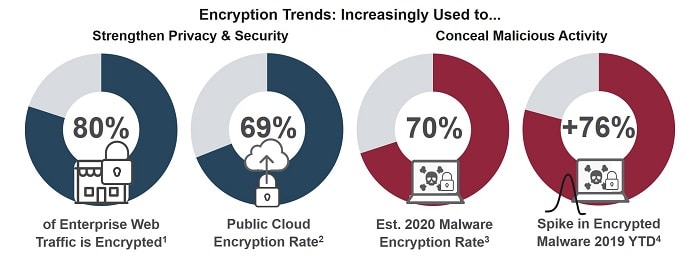
Why is Traffic Encryption on the Rise?
Everywhere you look, the use of encryption is rising: on the Internet, in public and private Clouds, within enterprises, and across personal devices. One driver of this trend is the global demand for better protection of personal privacy on the Internet. It is a demand that spiked in the wake of Snowden’s revelations about NSA interception activities, and has continued to mount ever since.
Protecting Personal Privacy – and Corporate Intellectual Property
This demand has been embraced by major content providers like Facebook, YouTube, and Netflix, who are responsible for the majority of encrypted Internet traffic today. Encryption helps them meet public demand for personal privacy, while enabling them to better protect their own intellectual property (IP).
Protecting IP and personal customer information is likewise fueling the increased use of encryption by enterprises. This includes the use of encryption behind the firewall as well as across the wide network of data centers, public and private cloud providers, and mobile operators who comprise the contemporary enterprise network.
Complying with Regulations
Companies and their service providers have also turned to encryption to satisfy regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Network and Information Security (NIS) Directive and EPrivacy.
Add to this voluntary initiatives like “Let’s Encrypt” and “Encryption Everywhere” by the Internet Security Research Group (ISRG) and Symantec respectively, and evolving Internet standards like HTTP Public Key Pinning (HPKP) and HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS), and the trend toward ubiquitous traffic encryption seems almost inevitable.
Who Else Likes Encryption? The Bad Guys
SonicWall’s 2019 Mid-Year Threat Report found 2.4 million encrypted malicious attacks in the first six months of 2019, almost eclipsing the 2018 full-year total in half the time. And this follows on the heels of a 27% increase in the use of encryption for malware and other malicious attacks in 2018.
Within the enterprise, encryption is also increasingly used by wayward employees intent on stealing valuable company, product or customer information.
Encryption & Traffic Classification
Identifying and classifying network traffic has long played a key role in protecting businesses and their ecosystem of digital service providers from such malicious internal or external attacks.
Traffic classification has also been critical to enforcing policy, optimizing traffic flows, meeting quality of service targets, and generating revenue through differentiated service offerings.
Are these benefits poised to disappear with the rise of encryption? No. In fact, given the rise in encryption, classification technology is more important than ever.

Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) to the Rescue
It is important to remember that encryption does not mean that the traffic is undetectable; it just means that the content remains private. Network traffic analysis using advanced technologies like Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) can still classify encrypted traffic, enabling protection, compliance and innovation to continue in the encryption age.
The primary aim of a DPI engine is to classify applications and services independently from the underlying (transport) protocols, these being encrypted or not.

How Qosmos’ DPI Engine Classifies Encrypted Data
To achieve this goal, Enea’s Qosmos Labs have reverse engineered the most important L4 and L7 protocols to identify key invariants that are used to classify the top applications.
Among these protocols are those adding encryption layers such as TLS (1.1, 1.2 and 1.3), dtls, quic, spdy and http2. Furthermore, Enea Qosmos technology uses DNS caching as well as statistical traffic models as a means to identify remaining traffic.
Here are a few examples of encrypted traffic classification techniques with indications of their accuracy and limitations.

Example 1: Classifying traffic encrypted with SSL/TLS (e.g. https)
Typical protocols: Google, Facebook, WhatsApp
Classification method: Read name of service in SSL/TLS certificate or in Server Name Indication (SNI)
Accuracy: Deterministic method – 100% accurate
Limitations: If SNI does not appear at the start of the handshake, the SSL/TLS certificate may only be available after 5 or 6 packets, which can cause a slight delay. Depending on the content provider, the same certificate may be used for different services (like email, news etc.).
Important: It is of common belief that TLS 1.3 makes traffic undetectable with current techniques. In the latest draft of TLS 1.3 (draft-ietf-tls-tls13-23), the SNI remains clear and is even exchanged in the session resumption processes (0 or 1 RTT). This means that current classification techniques, including those used by Qosmos ixEngine®, will continue to be effective.
Example 2: Classifying encrypted P2P
Typical protocols: BitTorrent (RC4 Encrypted), Ares
Classification method: Statistical Protocol Identification (SPID)
Statistical protocol identification is a technique based on divergence measurement of the traffic being analyzed and a statistical traffic model. Qosmos technology uses a statistical traffic model specially developed in-house.
Accuracy: Typically more than 90% of P2P sessions are identified for RC4 encrypted BitTorrent.
Additional info: This technique requires more packets than others (typically 15 for BitTorrent) in order to have a correct traffic model for matching.
Example 3: Classifying Skype
Classification method: Search for binary patterns in traffic flows
This pattern is usually found in the first 2 or 3 packets
Accuracy: 90 – 95 % accurate
Additional info: In addition to the search for binary patterns, a statistical method is used to identify different services within Skype such as Skype voice, Skype video, and Skype chat. This method uses a combination of jitter, delay, length of packets, spacing of packets, etc.
Thanks to advanced classification techniques, traffic optimization, policy enforcement, and user experience are largely unaffected by encryption. This means that communication service providers can continue to leverage network intelligence to ensure service quality and manage resource utilization, while respecting subscriber privacy.
In addition, when combined with machine learning and advanced analytics in Network Traffic Analysis solutions, DPI can help companies detect malicious activities that would otherwise go unnoticed under the cloak of encryption.
1. Gartner, Inc.
2. Ibid, Gartner.
3. SonicWall, Inc.
4. Ibid, SonicWall





